
Whether salaried individual or business owner, every person who is liable to pay income tax definitely tries to minimize the tax liability, at least for once. Even though it is unethical to save income tax and not pay the required tax amount as per your income, taxpayers still choose the following ways to minimize their tax liability;
Although these terms may sound similar and they also have a similar objective of minimizing the tax liability, but technically they are very different from each other and here’s the difference between tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion.
Tax Planning
Tax Avoidance and
Tax Evasion
What Is Tax Planning?
Tax planning is a completely logical and legal way of minimising one’s tax liability by availing the benefits of all the concessions, provisions, deductions and exemptions provided under the Income Tax Act.
Tax planning involves activities like income analysis, restructuring and investing, as particular investments made for a particular period can help the taxpayer avail a tax deduction. Life Insurance, Health Insurance, Fixed Deposits, Provident Funds, Mutual Funds and National Saving Certificate are taxpayer’s some of the most preferred ways of making investments.
For business owners, choosing the type of business organisation, its capital structure and the products or services also helps in getting the tax benefits by the government for particular sectors. Also, purchasing the machinery instead of renting it helps the business owner in availing the benefit of depreciation.
In India, taxpayers commonly make use of Section 80C to reduce their tax liability. As per Section 80C, if certain specified investments are made for a specified period, they can avail tax deduction for the same up to a limit of Rs. 1,50,000. The most common tax-saving instruments are investments in PPF Accounts, Tax Saving Fixed Deposit, National Savings Certificate, Provident Fund, Mutual Funds etc.
The primary aim of tax planning is not only to save taxes by any means, but to develop a long term, multi-faceted, logical and legal strategy that continues to channelise your income and optimise your taxes for years and years.
While paying taxes is your duty, you can use provisions within the law to reduce the amount that you pay as tax. Fintoo’ s experts help you with this so that you can save more and utilize the amount smartly for your goals and responsibilities.
Tax Avoidance:
Tax avoidance primarily is an act of minimising one’s tax liability by using legitimate methods that are within the limits of law or methods that do not break the law. Though tax avoidance also helps a taxpayer to minimise the tax liability like tax planning, but it is not as simple, straightforward and advisable as tax planning.
The activities in tax avoidance primarily focus on taking unfair advantages of the loopholes or lacunae in the income tax laws and manipulating the accounts in ways that help to avoid the taxes without breaking any rules or laws.
Though the process of tax avoidance does not break any laws or rules, but in some cases that reflect acts like;
- Disclosing / Reporting less income
- Hiding important facts related to tax calculation
- Showing fake transactions that do not relate to their true purpose
- Using fabricated contracts and statements
- Channelizing the funds through fake offshore branches
Tax avoidance may be included under the categories of fraud and crime.
What Is Tax Evasion?
Tax evasion is the activity in which an individual or an organisation deliberately underreports the income, inflates the deductions and shows bogus expenses in order to minimise the tax liability.
Moreover, acts like not reporting cash transactions and hiding money in offshore accounts, are also termed as techniques of tax evasion.
Unlike tax avoidance which may or may not come under the category of fraud or crime, tax evasion is undoubtedly considered as a crime and the individual or organization opting the means of tax evasion to save the taxes are liable to face prosecution in criminal court and may be given a stringent punishment in the form of a heavy fine or imprisonment or both.
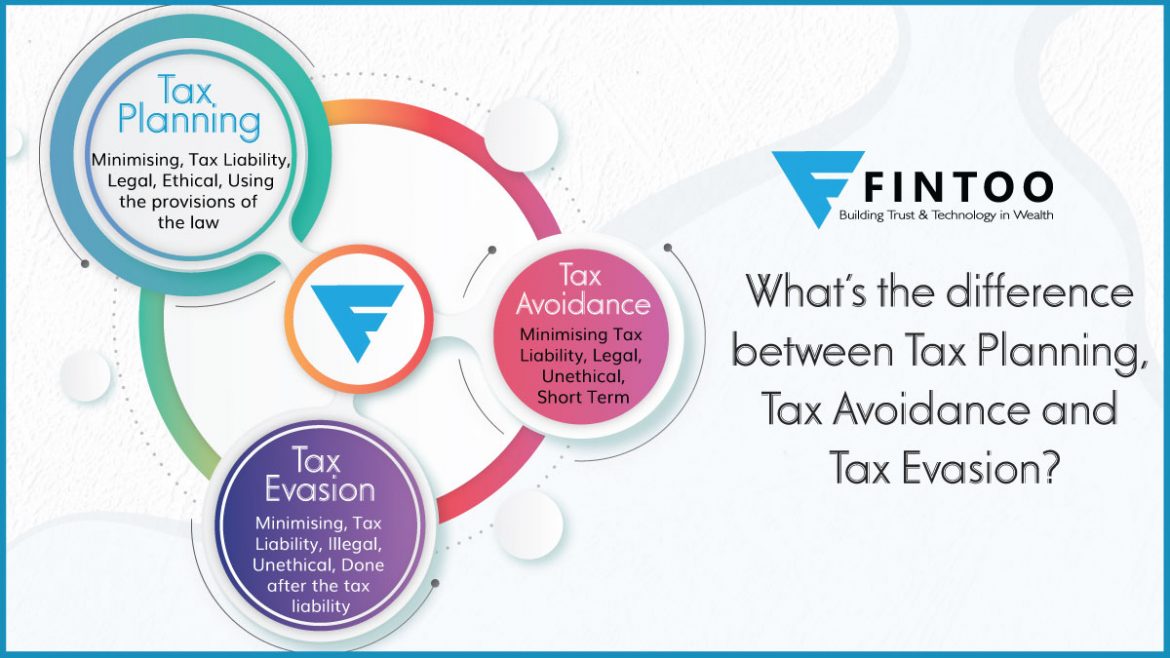
What’s The Difference Between Tax Planning, Tax Avoidance and Tax Evasion?
| Tax Planning | Tax Avoidance | Tax Evasion |
| Minimising Tax Liability | Minimising Tax Liability | Minimising Tax Liability |
| Legal | Legal | Illegal |
| Ethical | Unethical | Unethical & Illegal |
| Using the provisions of the law | Using loopholes in the law and manipulating the accounts | Disclosing wrong or misleading information |
| No Penalty | Penalty or imprisonment or both if violating the tax laws | Penalty or imprisonment or both |
| Long Term | Short Term | Short Term |
Request To The Tax Payers:
Considering the complications, confusions and technicalities in the taxation system, the knowledge about the taxation process is extremely limited when it comes to regular salaried individuals or even business owners. This lack of information leads the taxpayers whose only priority is to save taxes, unintentionally get involved in tax manipulations or tax frauds.
Therefore, it is extremely important for every taxpayer to at least understand the basic information related to the taxation requirements, processes and laws that apply to their current income and professional category. Also, consider taking a second opinion from another tax expert, especially during situations that involve legalities.
Which Is The Best Way To Reduce Tax?
Amongst tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion, wherein all the three focuses on minimising the tax liabilities, it is suggested that in the long term, tax planning is the logical, legal and best way to save taxes as well as to stay away from any legal trouble that may lead to a stringent punishment like heavy fine, imprisonment or both.
And if you wish to start tax planning, you can connect with the #TAXperts at Fintoo and get all the required information.
Related Article: How To Find Out Which ITR Form To Fill?
Fill in the details and our Income Tax Filing experts will get in touch with you. Hassle-Free Online ITR Filing with Fintoo! Start e-Filing
Disclaimer: The information shared in this article is generic in nature and for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for specific advice in your own circumstances. You are recommended to obtain specific professional advice before you take any/refrain from any action. Tax benefits are subject to changes in tax laws. Please contact your tax consultant for an exact calculation of your tax liabilities. All the views expressed in the article are solely of the writer and the company in no way endorses them or is related to them.
Related Posts
Stay up-to-date with the latest information.